Table of Contents
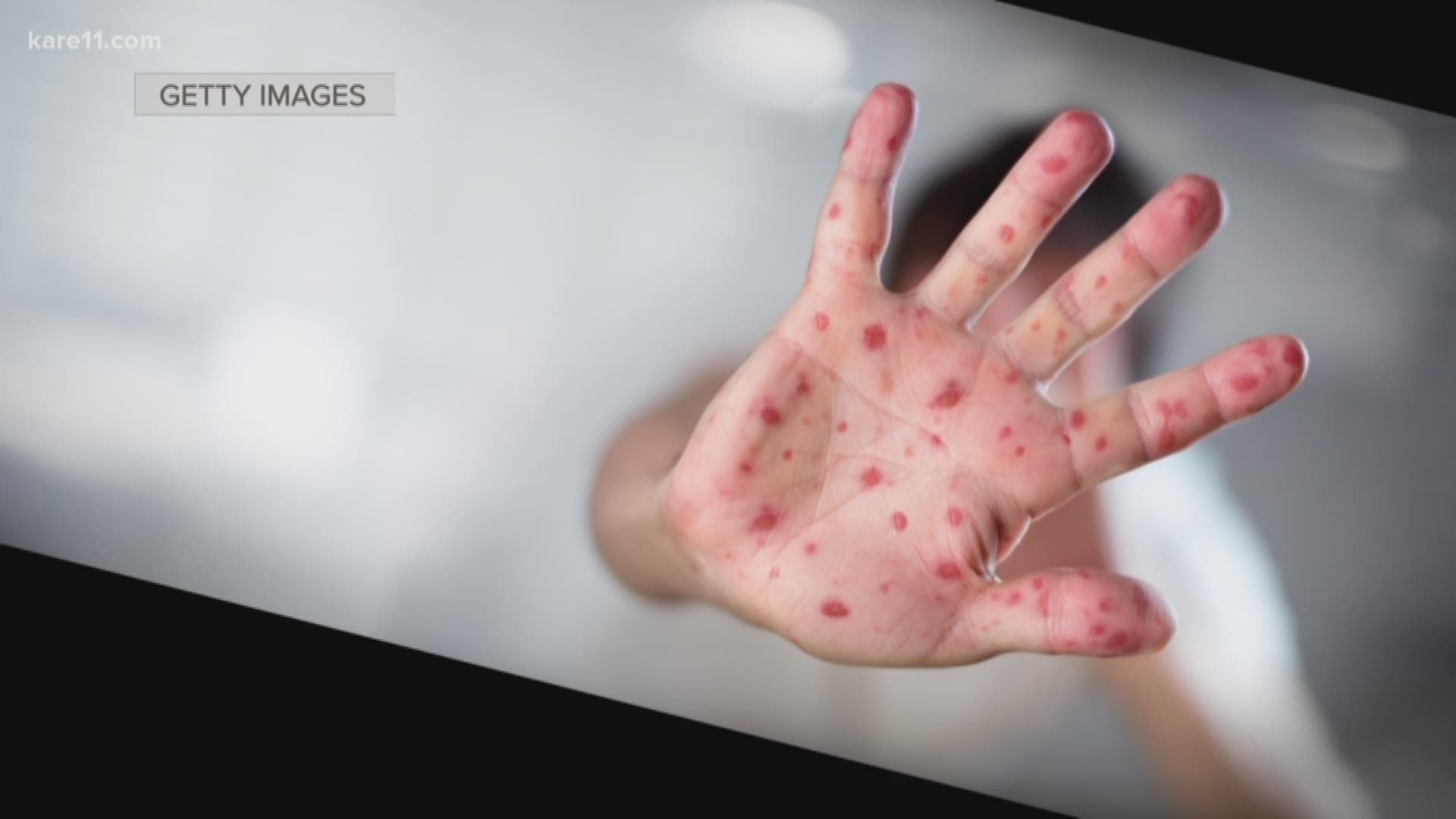
- Chickenpox 1 - “Chickenpox” Every year, there is a growing population ...
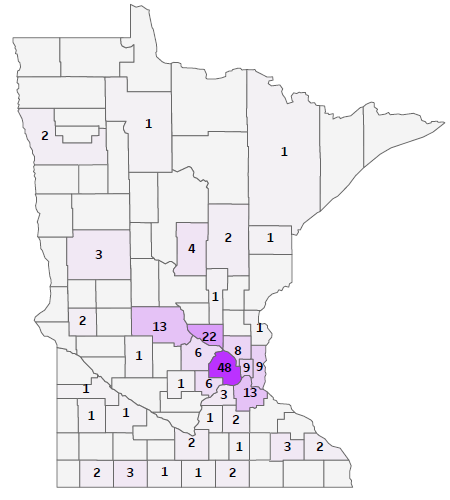
- Chickenpox weekly cases in Hungary reported between 2005 and 2015 ...
- The importance behind the chickenpox vaccine | kare11.com
- Varicella (Chickenpox) and Zoster (Shingles) Statistics - MN Dept. of ...
- Declining incidence of chickenpox in the absence of universal childhood ...
- Another big spike in hospitalizations as Minnesota's flu season worsens ...
- Chickenpox Cases | Kaggle
- Outbreaks of measles and chickenpox in eastern Uttar Pradesh, India ...
- Deaths from chickenpox | The BMJ
- Minnesota Department of Health reports first mpox cases of 2023 : r ...


Types of Infectious Diseases in Hennepin County


- Respiratory diseases: such as influenza, pneumonia, and tuberculosis, which can spread through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Gastrointestinal diseases: such as norovirus, salmonella, and E. coli, which can spread through contaminated food and water.
- Vaccine-preventable diseases: such as measles, mumps, and whooping cough, which can spread through person-to-person contact.
- Vector-borne diseases: such as Lyme disease and West Nile virus, which can spread through the bite of an infected tick or mosquito.


Causes and Symptoms of Infectious Diseases


- Person-to-person contact: through touching, shaking hands, or sharing personal items.
- Contaminated food and water: through consuming undercooked or raw foods, or drinking contaminated water.
- Vector-borne transmission: through the bite of an infected tick or mosquito.
- Airborne transmission: through inhaling droplets that contain pathogens.
- Fever
- Chills
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Body aches
Prevention and Control Methods
To prevent the spread of infectious diseases in Hennepin County, residents can take several steps, including:- Getting vaccinated: against vaccine-preventable diseases such as influenza, measles, and whooping cough.
- Practicing good hygiene: such as washing hands frequently, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.
- Avoiding contaminated food and water: such as consuming cooked foods, avoiding raw or undercooked meats, and drinking bottled or filtered water.
- Using insect repellent: to prevent vector-borne diseases such as Lyme disease and West Nile virus.
- Surveillance and monitoring: of disease outbreaks and trends.
- Investigation and response: to disease outbreaks, including contact tracing and vaccination efforts.
- Education and outreach: to inform residents about the risks of infectious diseases and the importance of prevention methods.